INDIVIDUALIZE CURRENT THERAPY BASED ON PATIENT NEED AND RESPONSE TO PRIOR THERAPY TO ACHIEVE TREATMENT GOALS
The International Consensus Report on ITP recommends individualized treatment goals
An individualized treatment strategy is needed for patients since ITP is a distinctly heterogeneous disease.
ITP=immune thrombocytopenia.
ITP is a heterogeneous disease with a complex, multifactorial pathogenesis
ITP is driven by 2 factors: immune-mediated platelet destruction and limited platelet production3
-
Dysregulation of the immune system leads to production of anti-platelet antibodies

-
Macrophage recognition of antibody-coated platelets results in unregulated platelet destruction
-
Lysis process results in an amplified production of anti-platelet antibodies
-
Platelet destruction causes decreased levels of thrombopoietin (TPO)

-
Anti-platelet antibodies may also target megakaryocytes, resulting in impaired megakaryocyte function
-
Irregular T-cell response may destroy platelets in bone marrow and impede platelet production
TAVALISSE offers a novel approach to treating chronic ITP
Limit platelet destruction with the targeted mechanism of TAVALISSE6,7
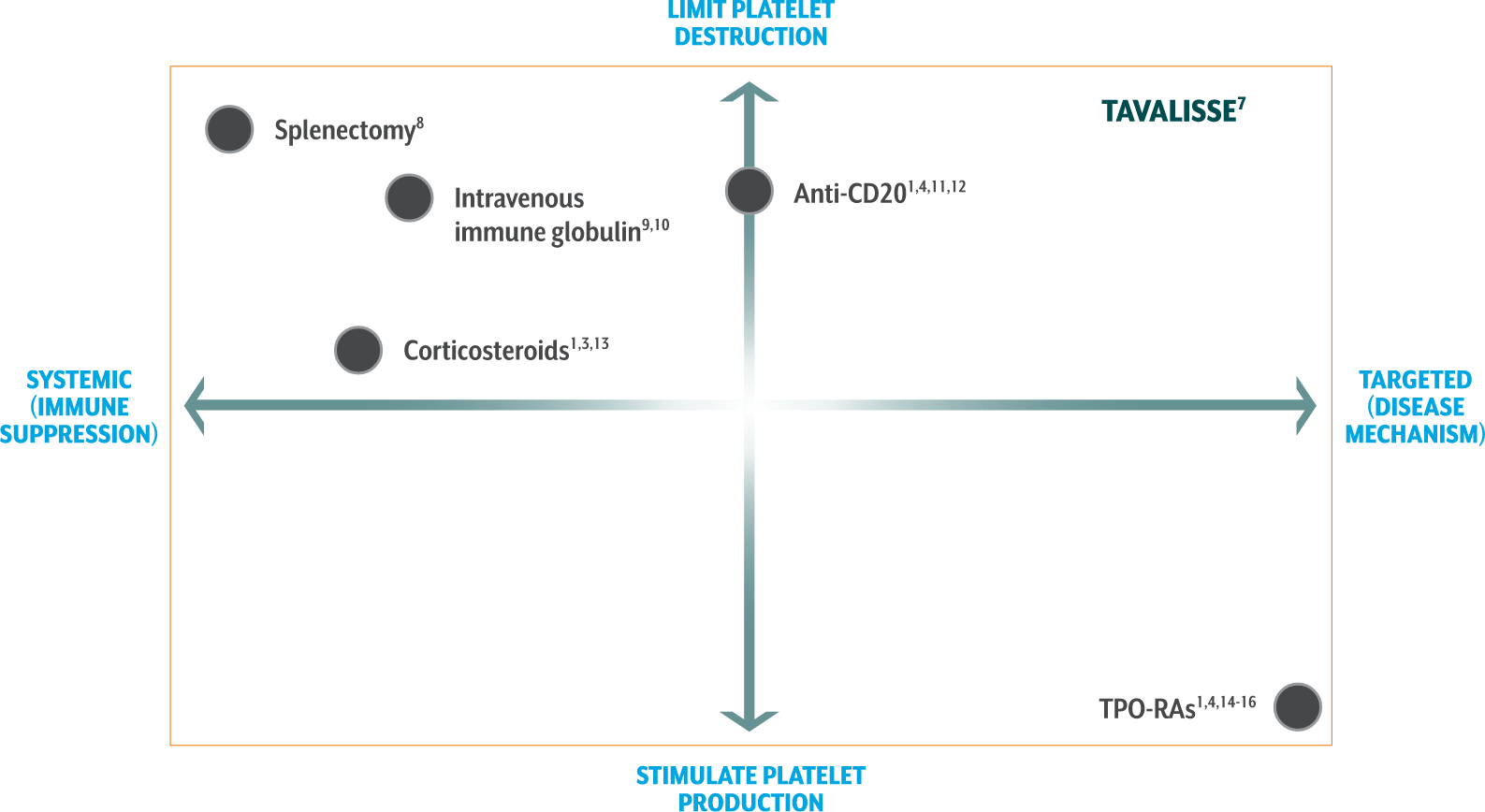
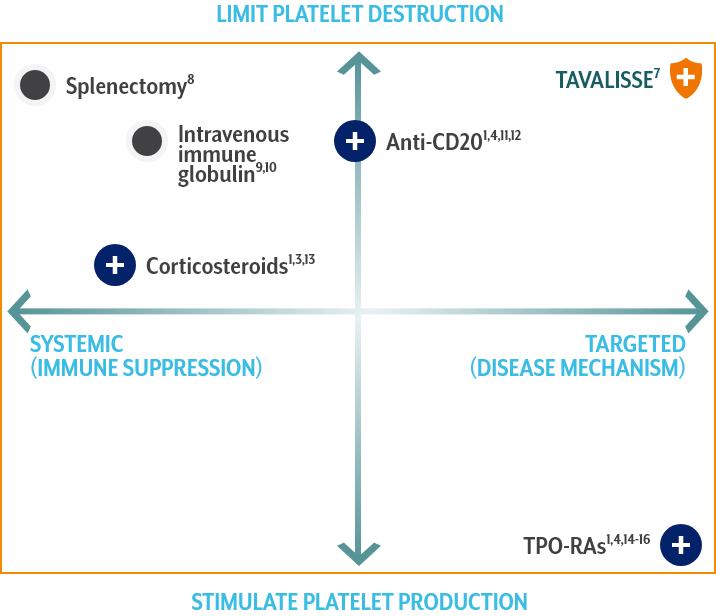
TAVALISSE7
TAVALISSE is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment.
Corticosteroids1,3,13
- Suppress systemic function and reduce antibody production, resulting in decreased platelet destruction
- Standard 1st-line therapy for recently diagnosed patients
- Over time, treatment side effects may outweigh the potential benefits
- Most patients relapse upon discontinuation of treatment
Anti-CD201,4,11,12
- Depletes B cells
- Increased response when used with concomitant corticosteroids
- A meta-analysis of 5 trials showed that rituximab was not associated with reductions in bleeding
- In a study of response durability, only 21% maintained remission at 5 years
TPO-RAs1,4,14-16
- Stimulate megakaryocytes in bone marrow to produce platelets
- Associated with potential increases in bone marrow fibrosis
- Evidence of increased thrombotic events with use of certain TPO-RA agents
TPO-RAs=thrombopoietin receptor agonists.
[TAVALISSE] has a unique mechanism of action, dissimilar to other approved ITP therapies, and produced responses in patients who had relapsed or not responded to TPO-RA agents, rituximab, and/or splenectomy.
References: 1. Provan D, Arnold DM, Bussel JB, et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019;3(22):3780-3817. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000812 2. Shih A, Nazi I, Kelton JG, Arnold DM. Novel treatments for immune thrombocytopenia. Presse Med. 2014;43:e87-e95. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2014.02.006 3. Raj AB. Immune thrombocytopenia: pathogenesis and treatment approaches. J Hematol Transfus. 2017;5(1):1056-1065. 4. Newland A, Lee E, McDonald V, Bussel JB. Fostamatinib for persistent/chronic adult immune thrombocytopenia. Immunotherapy. 2018;10(1):9-25. doi:10.2217/imt-2017-0097 5. Olsson B, Ridell B, Carlsson L, Jacobsson S, Wadenvik H. Recruitment of T cells into bone marrow of ITP patients possibly due to elevated expression of VLA-4 and CX3CR1. Blood. 2008;112(4):1078-1084. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-02-139402 6. Bussel J, Arnold DM, Grossbard E, et al. Fostamatinib for the treatment of adult persistent and chronic immune thrombocytopenia: results of two phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(7):921-930. 7. TAVALISSE®. Package insert. Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 8. Ghanima W, Godeau B, Cines DB, Bussel JB. How I treat immune thrombocytopenia: the choice between splenectomy or a medical therapy as a second-line treatment. Blood. 2012;120(5):960-969. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-12-309153 9. Kistangari G, McCrae KR. Immune thrombocytopenia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013;27(3):495-520. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2013.03.001 10. WinRho® SDF [package insert]. Roswell, GA: Saol Therapeutics, Inc.; July 2019. 11. Stasi R, Pagano A, Stipa E, Amadori S. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment for adults with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura. Blood. 2001;98(4):952-957. doi:10.1182/blood.v98.4.952 12. Rituxan® [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc.; June 2021. 13. Mizutani H, Furubayashi T, Imai Y, et al. Mechanisms of corticosteroid action in immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): experimental studies using ITP-prone mice, (NZW x BXSB) F1. Blood. 1992;79(4):942-947. 14. Doptelet® [package insert]. Durham, NC: AkaRx; July 2021. 15. Nplate® [package insert]. Thousand Oaks, CA: Amgen, Inc.; February 2022. 16. Promacta® [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; October 2021.
